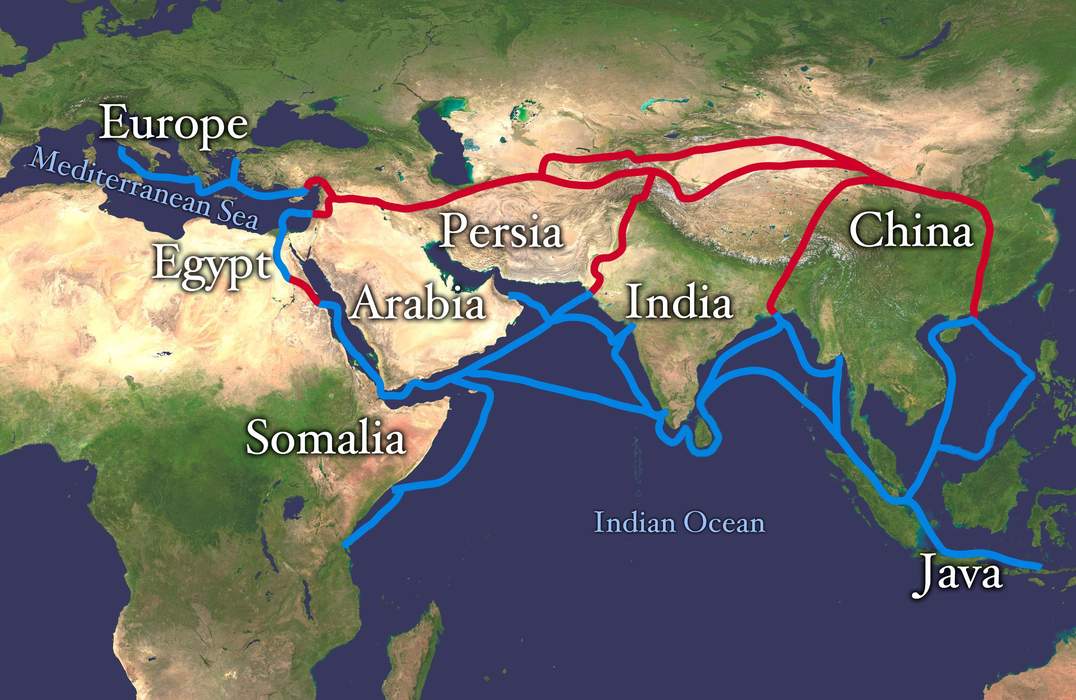
The
Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 km (4,000 mi), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the Eastern and Western worlds. The name "Silk Road" was coined in the late 19th century, but some 20th- and 21st-century historians instead prefer the term
Silk Routes, on the grounds that it more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting Central, East, South, Southeast, and West Asia as well as East Africa and Southern Europe.


